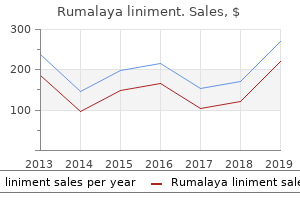
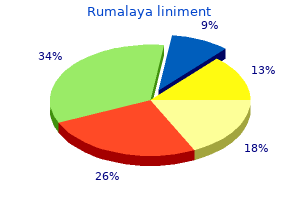
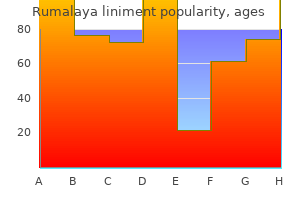
"Buy generic rumalaya liniment 60 ml online, spasms define".
By: I. Cyrus, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Professor, Saint Louis University School of Medicine
About 50% of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism are asymptomatic while others have non-specific symptoms such as fatigue muscle relaxant clonazepam order rumalaya liniment 60 ml on line, depression and generalised aches and pains muscle relaxant and nsaid buy rumalaya liniment 60ml with mastercard. High plasma phosphate and alkaline phosphatase accompanied by renal impairment suggest tertiary hyperparathyroidism xanax muscle relaxant dosage cheap 60 ml rumalaya liniment with visa. Hypercalcaemia may cause nephrocalcinosis and renal tubular impairment, resulting in hyperuricaemia and hyperchloraemia. Unless the source is obvious, the patient should be screened for malignancy with a chest X-ray, myeloma screen (p. Of these, primary hyperparathyroidism and malignant hypercalcaemia are by far the most common. Lithium may cause hyperparathyroidism by reducing the sensitivity of the calciumsensing receptor. Conversely, ionised calcium may be low in the face of normal total serum calcium in patients with alkalosis: for example, as a result of hyperventilation. Hypocalcaemia may also develop as a result of magnesium depletion and should be considered in patients with malabsorption, those on diuretic or proton pump inhibitor therapy, and/or those with a history of alcohol excess. This is characterised by muscle spasms due to increased excitability of peripheral nerves. Children are more liable to develop tetany than adults and present with a characteristic triad of carpopedal spasm, stridor and convulsions, although one or more of these may be found independently of the others. Adults can also develop carpopedal spasm in association with tingling of the hands and feet and around the mouth, but stridor and fits are rare. Prolonged hypocalcaemia and hyperphosphataemia (as in hypoparathyroidism) may cause calcification of the basal ganglia, grand mal epilepsy, psychosis and cataracts. Hypocalcaemia associated with hypophosphataemia, as in vitamin D deficiency, causes rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults (p. Osteitis fibrosa results from increased bone resorption by osteoclasts with fibrous replacement in the lacunae. Chondrocalcinosis can occur due to deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals within articular cartilage. It typically affects the menisci at the knees and can result in secondary degenerative arthritis or predispose to attacks of acute pseudogout (p. Skeletal X-rays are usually normal in mild primary hyperparathyroidism, but in patients with advanced disease characteristic changes are observed. In the early stages there is demineralisation, with subperiosteal erosions and terminal resorption in the phalanges. Reduced bone mineral density, resulting in either osteopenia or osteoporosis, is now the most common skeletal manifestation of hyperparathyroidism. There may be soft tissue calcification in arterial walls and hands and in the cornea. This is most commonly seen in individuals with advanced chronic kidney disease (p. A After 1 hour, there is uptake in the thyroid gland (thick arrow) and the enlarged left inferior parathyroid gland (thin arrow).
Psammoma bodies and spasms spinal cord injury buy rumalaya liniment with visa, in rare cases spasms small intestine order rumalaya liniment with visa, eosinophilic strap-shaped cells resembling rhabdomyoblasts have been encountered muscle relaxant 10mg cheap rumalaya liniment generic. Hyperplastic mesothelial cells may rarely involve intra-abdominal lymph nodes, a finding that has been associated with, and in such cases is presumably secondary to , mesothelial hyperplasia of the peritoneum. Cytokeratin staining in such cases may reveal more extensive involvement of the lymph node by the mesothelial cells than is appreciable in routinely stained sections. Differential Diagnosis the major differential diagnosis of mesothelial hyperplasia is malignant mesothelioma. The presence of grossly visible nodules, necrosis, conspicuous large cytoplasmic vacuoles, severe nuclear atypia, and deep infiltration favors mesothelioma over mesothelial hyperplasia. Note the linear arrangement of the mesothelial cells within inflamed fibrous tissue. The hyperplastic mesothelial cells were adjacent to a mucinous borderline tumor and were misinterpreted as foci of invasion. In addition to mesothelioma, the differential diagnosis of peritoneal or intranodal mesothelial hyperplasia includes serous borderline tumors, in the form of spread from an ovarian serous borderline tumor or a primary peritoneal or intranodal serous borderline tumor (see section on Peritoneal Serous Lesions). Grossly visible ovarian or peritoneal tumor nodules, columnar cells that may bear cilia, the presence of intracellular or extracellular neutral mucin, and numerous psammoma bodies favor a serous borderline tumor. Immunoreactivity for epithelial antigens (see later section on malignant mesothelioma) is also useful in the differential diagnosis. Peritoneal Inclusion Cysts Peritoneal inclusion cysts usually occur in women of reproductive age,10-24 but the same lesions occur rarely in males or have involved the pleura. They occasionally involve the round ligament, potentially mimicking an inguinal hernia. Most unilocular mesothelial cysts are probably reactive in origin, although developmental origin has been suggested for at least some of those cases involving the mesocolon, mesentery of the small intestine, retroperitoneum, and splenic capsule. Typically they are adherent to pelvic viscera and may mimic a cystic ovarian tumor clinically, intraoperatively,13 or on pathologic examination; the upper peritoneal cavity, the spleen,18 the liver,20 the retroperitoneum, the inguinal region,21 and hernia sacs also can be involved. The mesothelial cells may proliferate into the cyst lumina as small papillae or in cribriform patterns, and occasionally they may undergo squamous metaplasia. We therefore prefer the designation multilocular peritoneal inclusion cyst to benign cystic mesothelioma for these lesions. Note inflamed stroma and occasional hobnail-like mesothelial cells lining the cysts. Peritoneal Keratin Granulomas Infectious and noninfectious peritoneal granulomas are almost always readily distinguishable from a neoplasm on microscopic examination. Although follow-up data have shown that these granulomas have had no effect on the prognosis, the prognostic significance of these lesions has not been established with complete certainty because of the short follow-up interval in some cases and because some of the patients have received postoperative radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or both. Keratin granulomas, if visible, should be sampled extensively by the surgeon and assiduously examined microscopically by the pathologist to exclude the additional presence of any viable carcinoma cells. The differential diagnosis includes peritoneal granulomas in response to keratin derived from other sources, including amniotic fluid and ovarian dermoid cysts. In the latter situation, cyst rupture releases sebaceous material and keratin that typically evoke an intense granulomatous, lipogranulomatous, and fibrosing peritoneal inflammatory reaction that may mimic a neoplasm at operation. Fibrotic thickening of the omental surface and its interlobular septa can be seen. A reactive peritoneal fibrotic lesion may contain multipotential subserosal cells28 that take the form of plump, often fasciitis-like spindle cells that immunoreact for vimentin, smooth muscle actin, and cytokeratin. Sclerosing peritonitis is a rare disorder characterized by fibrous peritoneal thickening that can encase the small bowel (abdominal cocoon), causing bowel obstruction. Although it may be idiopathic (such cases typically occur in adolescent girls), common etiologic associations include practolol therapy, chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, the use of a peritoneovenous (LeVeen) shunt, and fibrothecomatous proliferations of the ovary (typically, luteinized thecoma).
The most serious manifestation of lupus is an acute alveolitis that may be associated with diffuse alveolar haemorrhage spasms pancreas buy 60 ml rumalaya liniment overnight delivery. This condition is life-threatening and requires either immediate immunosuppression with glucocorticoids or a step-up in immunosuppressive treatment muscle relaxant bodybuilding buy rumalaya liniment 60 ml overnight delivery, if already started spasms esophagus problems generic 60 ml rumalaya liniment visa. The chest X-ray reveals elevated diaphragms and pulmonary function testing shows reduced lung volumes. Rarely, the potentially fatal condition called obliterative bronchiolitis may develop. The classical chest X-ray appearance has been likened to the photographic negative of pulmonary oedema with bilateral, peripheral and predominantly upper lobe parenchymal shadowing. Pulmonary eosinophilia refers to the association of radiographic (usually pneumonic) abnormalities and peripheral blood eosinophilia. Other pulmonary complications include recurrent aspiration pneumonias secondary to oesophageal disease. The condition presents with fever, weight loss, dyspnoea and asthma-like symptoms. The diagnosis may be confirmed by a response to treatment with diethylcarbamazine (6 mg/kg/day for 3 weeks). Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia must be distinguished from infection with Strongyloides stercoralis (p. Pulmonary disease usually precedes renal involvement and includes radiographic infiltrates and hypoxia with or without haemoptysis. Chronic interstitial fibrosis may present several months later with symptoms of exertional dyspnoea and cough. The lung is commonly involved in systemic forms of the disease but a limited pulmonary form may also occur. Associated upper respiratory tract manifestations include nasal discharge and crusting, and otitis media. Radiological features include multiple nodules and cavitation that may resemble primary or metastatic carcinoma, or a pulmonary abscess. Tissue biopsy confirms the distinctive pattern of necrotising granulomas and necrotising vasculitis. Other respiratory complications include tracheal subglottic stenosis and saddle nose deformity. Pulmonary fibrosis may occur in response to a variety of drugs but is seen most frequently with bleomycin, methotrexate, amiodarone and nitrofurantoin. The pathogenesis may be an immune reaction similar to that in hypersensitivity pneumonitis, which specifically attracts large numbers of eosinophils into the lungs. This type of reaction is well described as a rare reaction to a variety of antineoplastic agents. Most cases resolve completely on withdrawal of the drug, but if the reaction is severe, rapid resolution can be obtained with glucocorticoids. Drugs may also cause other lung diseases, such as asthma, pulmonary haemorrhage, pleural effusion and, rarely, pleural thickening. Prednisolone can usually be withdrawn after a few weeks without relapse but long-term, low-dose therapy is occasionally necessary. Renal involvement is more common at presentation and upper respiratory problems are fewer. A diagnosis therefore frequently depends on clinical and highresolution computed tomography findings alone.
B the velocity of the blood cells is recorded to determine the maximum velocity and hence the pressure gradient across the valve spasms constipation buy rumalaya liniment mastercard. It is particularly useful for imaging structures such as the left atrial appendage muscle relaxant anxiety buy 60 ml rumalaya liniment otc, pulmonary veins muscle relaxant without drowsiness order 60 ml rumalaya liniment otc, thoracic aorta and interatrial septum, which may be poorly visualised by transthoracic echocardiography, especially if the patient is overweight or has obstructive airway disease. Doppler echocardiography is useful in the detection of valvular regurgitation, where the direction of blood flow is reversed and turbulence is seen, and is also used to detect pressure gradients across stenosed valves. For example, the normal resting systolic flow velocity across the aortic valve is approximately 1 m/sec; in the presence of aortic stenosis, this is increased as blood accelerates through the narrow orifice. In severe aortic stenosis, the peak aortic velocity may be increased to 5 m/sec. An estimate of the pressure gradient across a valve or lesion is given by the modified Bernoulli equation: m m. Colour-flow Doppler has been used to demonstrate mitral regurgitation: a flame-shaped (yellow/blue) turbulent jet into the left atrium. Multidetector scanners can acquire up to 320 slices per rotation, allowing very high-resolution imaging in a single heart beat. Contrast scans are very useful for imaging the aorta in suspected aortic dissection. However, modern multidetector scanning allows non-invasive coronary angiography. Modern volume scanners are also able to assess myocardial perfusion, often at the same sitting. A two-dimensional echo is performed before and after infusion of a moderate to high dose of an inotrope, such as dobutamine. Myocardial segments with poor perfusion become ischaemic and contract poorly under stress, manifesting as a wall motion abnormality on the scan. Stress echocardiography is sometimes used to examine myocardial viability in patients with impaired left ventricular function. A Recent inferior myocardial infarction with black area of microvascular obstruction (arrow). B Old anterior myocardial infarction with large area of subendocardial delayed gadolinium enhancement (white area, arrows). Physiological data can be obtained from the signal returned from moving blood, which allows quantification of blood flow across regurgitant or stenotic valves. It is also possible to analyse regional wall motion in patients with suspected coronary disease or cardiomyopathy. When enhanced by gadolinium-based contrast media, areas of myocardial hypoperfusion can be identified with better spatial resolution than nuclear medicine techniques. Coronary angiography is the most widely performed procedure, in which the left and right coronary arteries are selectively imaged, providing information about the extent and severity of coronary stenoses, thrombus and calcification. This permits planning of percutaneous coronary intervention and coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Aortography defines the size of the aortic root and thoracic aorta, and can help quantify aortic regurgitation. Left heart catheterisation is a day-case procedure and is relatively safe, with serious complications occurring in only approximately 1 in 1000 cases. Right heart catheterisation is used to assess right heart and pulmonary artery pressures, and to detect intracardiac shunts by measuring oxygen saturations in different chambers. Making the correct diagnosis depends on careful analysis of the factors that provoke symptoms, the subtle differences in how they are described by the patient, the clinical findings and the results of investigations. A close relationship between symptoms and exercise is the hallmark of heart disease.
Order rumalaya liniment with a visa. Skelaxin (Metaxalone) - Pain Relief.