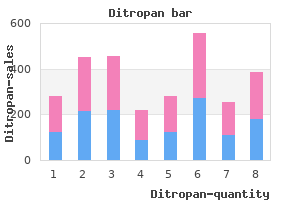
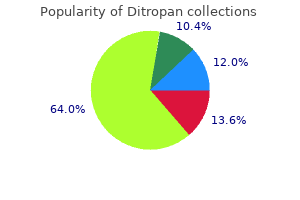
"Order ditropan once a day, gastritis diet íôòâó÷þêã".
By: M. Potros, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Program Director, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
The latter is relatively common in SouthEast Asia and gives rise to completely globin deficient homozygotes (- -/- -) with hydrops foetalis gastritis diet 2014 generic 5 mg ditropan fast delivery. The (-) haplotype is relatively common among Melanesians chronic gastritis diagnosis order discount ditropan on-line, having been selected by malaria (see Chapter 29) gastritis poop discount ditropan amex. This occurs as a consequence of two unusual conditions: (1) the existence of several copies of a small gene called A located near the Xq telomere, plus another within intron 22 of the F8 gene; and (2) the fact that the long arm of the X has no pairing homologue in male meiosis. As a consequence, internal recombination sometimes occurs following looping back of the end of the X. Breakage and rejoining within the A genes causes inversion of the intervening segment of the F8 gene (see Figure 25. Chemical mutagenesis Environmental mutagens include constituents of smoke, paints, petrochemicals, pesticides, dyes, foodstuffs, drugs, etc. Promutagens, such as nitrates and nitrites are converted into mutagens by body chemistry. Nitrous acid converts cytosine to uracil, and adenine to hypoxanthine, a precursor of guanine. Biological effects of radiation Electromagnetic radiation damages proteins and above 1 gray kills cells. X-rays damage chromosomes most readily when they are condensed, which is why they are most harmful to dividing cells, including the progenitors of sperm. At 1 Gy, X-rays cause a 50% reduction in white blood cell count, while whole-body irradiation of 4. Electromagnetic radiation Particulate discharge from radioactive decay includes alpha-particles (helium nuclei), beta-particles (electrons) and gamma-rays. The mutagenicity of subatomic particles depends on their speed, mass and electric charge. The energy and mutagenicity of electromagnetic radiation increases with decreasing wavelength. It exerts a mutagenic effect by causing dimerization (linking) of adjacent pyrimidine residues, mainly T-T (but also T-C and C-C). It does not cause germline mutations, but is a major cause of skin cancer, especially in homozygotes for the red hair allele (see Chapter 3), who have white, freckled skin. This corrects double-strand breaks either unguided, or by using the homologous chromosome as a template. These present a major theoretical hazard for aircrews, as their intensity increases with altitude. Exposure during a return flight between England and Spain is said to equal five chest X-rays. Radiation workers are at particular risk and periosteum-seeking isotopes present a major risk of leukaemia. The mechanism of imprinting is probably unique for each imprinted chromosomal region.
However gastritis symptoms burping best buy ditropan, both short and tall stature as well as macrocephaly and microcephaly have been seen more frequently than in the general population gastritis diet ðæä order ditropan online. Intellectual disability gastritis diet ðóòîð buy ditropan online, severe to profound in majority of cases; absent or severely delayed speech; hypotonia; frequent mouthing/ chewing of objects; autistic behavior. Dolichocephaly; full brow, long eyelashes, and full/puffy eyelids and cheeks; prominent, dysplastic ears; pointed chin. Nine affected individuals at birth, 6 months, 1 year (top row); 3 years, 5 years, 7 years (second row); 9 years, 13 years, and 24 years (third row). About 40 cases of Xq functional disomy due to cytogenetically visible rearrangements and more than 100 cases of cryptic duplications have been reported. Clinical manifestations vary depending on the gender and on the gene content of the duplicated segment. Recurrent infections, low serum IgA and IgM, elevated serum IgG, poor response to polysaccharide antigen, and poor T-cell response to Candida. Recurrent infections have decreased with the use of intravenous or subcutaneous immunoglobulins, although the specific immune defect underlying the infections has not been determined in most cases. Severe intellectual disability (99%), absence of speech or severely retarded speech (88%), major axial hypotonia (92%), progressive spasticity (59%) (most prominent in lower limbs), ataxia (54%), epilepsy (52%), autism spectrum disorders (76%), choreiform movements (45%). Hypoplasia of corpus callosum, mild brain atrophy/loss of cerebral volume, external hydrocephalus. Growth retardation, microcephaly and additional malformations (cardiac defects, genital anomalies), or more severe dysmorphic features are characteristic of larger deletions of Xq. Most Xq duplications observed in males are inherited from their mothers, although a few de novo duplications have been identified. In females, intrachromosomal duplications of the X chromosome are generally associated with a skewed inactivation pattern biased toward the duplicated X chromosome, leading to a normal or near-normal phenotype. However, some carrier females have a variety of neuropsychiatric phenotypes (depression, anxiety, compulsions, autistic features) but normal cognition. Occasionally, females can have short stature, developmental delay, facial dysmorphism, and gonadal dysgenesis. Sanlaville D, Schluth-Bolard C, Turleau C: Distal Xq duplication and functional Xq disomy, Orphanet J Rare Dis 4:4, 2009. Severe neonatal encephalopathy resulting in death before age 2 years is most frequent in affected males. References Sanlaville D, et al: Functional disomy of the Xq28 chromosome region, Eur J Hum Genet 13:579, 2005. B, Hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, depressed nasal bridge, upturned nares, small and open mouth, thin tented upper lip. As the molecular etiology of this condition has been elucidated, both a classical and a milder phenotype are recognized. Hirsutism (78%), cutis marmorata and perioral pale "cyanosis" (56%), hypoplastic nipples and umbilicus (50%), low posterior hairline (92%) Limbs. Micromelia (93%), phocomelia and oligodactyly (27%), clinodactyly of fifth fingers (74%), single transverse palmar crease (51%), proximal implantation of thumbs (72%), flexion contracture of elbows (64%), syndactyly of second and third toes (86%), cold extremities Genitalia. Hypoplasia in males (57%), undescended testes (73%), hypospadias (33%), hypoplastic labia majora Gastrointestinal. Mandibular spur present up to 3 months of age, dislocated/hypoplastic radial head, hypoplastic first metacarpal and fifth middle phalanx, short sternum with precocious fusion and 13 ribs, enlarged cerebral ventricles, white matter atrophy.
Discount 2.5 mg ditropan fast delivery. Foods to Avoid When Suffering From Gastritis! #Gastritis #Prevention #tips for All.
Autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system turns against the tissues of the same individual gastritis symptoms ayurveda purchase 5 mg ditropan otc. Type1Interferondeficiency Type 1 interferons are proteins produced by leucocytes in the frontline innate immune response against viral infection gastritis ranitidine cheap ditropan 2.5 mg without a prescription. They also play a role in induction of cytokines and stimulation of effector cells of the immune system gastritis diet dairy purchase ditropan 2.5 mg amex. Disorders of innate cell-mediated immunity Neutropenia the neutropenias are a heterogeneous group of disorders of innate cell-mediated immunity characterized by very low neutrophil counts. Patients develop pneumonia, lymph node infections and abscesses in the skin, liver, etc. Defects in complement C3 can cause failure of opsonization of bacteria, or upset the membrane attack complex (see Chapter 64), causing susceptibility to bacterial infection, especially by Neisseria (Meningococcus). Aetiology A defect in lysosome assembly causes deficiency specifically of natural killer cells. Since maternal IgG crosses the placenta, infants may be unaffected for several months. Genetic disorders of the immune system Immunogenetics 171 Management Prophylactic intravenous immunoglobulin. Aetiology DiGeorge syndrome is part of a spectrum of phenotypes caused by abnormalities of the third and fourth gill pouches consequent upon contiguous gene deletion in Chromosome 22q11. Complete or partial absence of the thymus reduces production of T cells allowing recurrent viral infections, which however usually decrease with age. Autosomal recessive B-cell immunodeficiency can be caused by mutation of the Ig heavy and light chains. There are low serum IgA and IgG levels and susceptibility to sinus and pulmonary infection. Lymphocyte chromosomes show rearrangements of Chromosomes 7 and 14 at the T-cell receptor loci (see Chapter 64). They show extraordinarily wide polymorphism, but are uniform within an individual. The peptides are derived by proteolytic degradation of endogenous antigens, derived for example from intracellular viruses, by the action of a large multifunctional protease (see Chapters 64 and 65). They occur on B cells and macrophages and are involved in presenting peptides to helper T cells (Figure 64. Some 20 loci affect cytokine levels, signalling pathways in immune cells and non-immunological steps in tissue damage. Selfrecognizing B lymphocytes are likewise eliminated in the bone marrow, although some may survive if the self-antigen concentration is low. Presentation of microbial products to T cells by immature dendritic cells lacking the full complement of co-stimulatory molecules may constitute a negative signal, so inducing tolerance. In addition, T cells contribute to tolerance by sometimes transmitting negative signals. This genetic association is thought to involve interference with the normal immune response to the bacterium Klebsiella. Its persistent inhibition is associated with apoptosis, abnormal immune cell development and delayed cell growth. Tissue incompatibility in transfusion and transplantation As a general rule a recipient will reject a tissue graft from a person who possesses a cell surface antigen absent from the recipient.
The eyelid fusion bands histologically are composed of a central core of vascular connective tissue entirely surrounded by epithelium gastritis hypertrophic buy discount ditropan 5 mg line. These bands may represent abnormal proliferation of mesenchymal tissue at certain points on the lid margin or an ectodermal deficit allowing mesodermal union gastritis diet 50\/50 buy ditropan 5 mg with amex. Oval face; absence of lacrimal puncta; ocular hypotelorism; broadened nasal bridge; maxillary hypoplasia; micrognathia; thin vermillion border; cleft lip gastritis diet 4 days purchase ditropan online now, cleft palate, or both; short philtrum; conical, widely spaced teeth; hypodontia to partial anodontia; ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum; hypoplastic alae nasi; small ears. Palmar and plantar keratoderma; peeling erythematous, eroded skin at birth from limited to high percentage of body surface area; hyperkeratosis; patchy, partial deficiency of sweat glands; partial anhidrosis; hyperpigmentation. Wiry and sparse to alopecia; head and/or eyelashes both affected; hypoplasia of lateral one third of eyebrows. Syndactyly of the second and third toe and of the third and fourth toe; syndactyly of the third and fourth finger; internal toe deviation; broad first toe. Surgical closure of facial clefting and early ophthalmologic evaluation of the lacrimal duct system are required. Severe chronic granulomas of the scalp, which begin as infections, have been a serious References Duke-Elder S: Textbook of Ophthalmology, vol 5, London, 1952, Kimpton. Fomenkov K, et al: P63 Mutations lead to aberrant splicing of the keratinocyte growth factor receptor in the Hay-Wells syndrome, J Biol Chem 278:23906, 2003. Freeman and colleagues reported five cases and reviewed the features in the 17 previously recognized patients. The majority of the survivors have had marked growth deficiency, and some have had severe intellectual disability. Birth length greater than 37 cm, less severe limb defects, absence of cleft palate, and presence of thin nares have been associated with a better prognosis. Ten adults, the majority of whom have had typical limb defects, craniofacial anomalies, growth retardation, and intellectual disabilities, have been reported. Additional features noted in adults include cardiac defects, particularly aortic stenosis; ocular findings in addition to corneal clouding, including cavernous hemangioma, paracentral scotoma and pits, tilting of the optic nerve, and bilateral optic nerve atrophy; one case of malignant melanoma and a possible increased risk for veno-occlusive disease. Profound growth deficiency of prenatal onset, birth weight in full-term infants 1. Cleft lip with or without cleft palate and prominent premaxilla, hypertelorism (87%), midfacial capillary hemangioma (78%), thin nares, shallow orbits and prominent eyes (69%), bluish sclerae, corneal clouding (68%), micrognathia, malformed ears with hypoplastic lobules. Hypomelia, more severe in upper limbs, varying from tetra-amelia to tetraphocomelia to lesser degrees of limb reduction, often including reduction in length or absence of the humerus (77%), radius (98%), or ulna (96%); reduction in number or length of fingers (75%), syndactyly (42%), or clinodactyly; reduction or absence of femur (65%), tibia (74%), or fibula (80%); reduction in number of toes (27%); incomplete development of dermal ridges; flexion contractures of knees, ankles, wrists, or elbows. Appelt H, Gerken H, Lenz W: Tetraphokomelie mit LippenKiefer-Gaumenspalte und Clitorishypertrophie-Ein Syndrome, Paediatr Paedol 2:119, 1966. Waldenmaier C, Aldenhoff P, Klemm T: the Roberts syndrome, Hum Genet 40:345, 1978. Note capillary hemangioma on forehead in infancy and sparse scalp hair as a child. This unique pattern of defects has been noted subsequently in numerous cases and has an incidence of approximately 1 in 20,000. It has been estimated that 10% of patients with syndactyly of the hand have the Poland sequence. Credence for a vascular pathogenesis comes from the suggestion that maternal smoking may increase the risk by approximately twofold. Although the vast majority of cases are sporadic, the incidence of familial transmission has been as high as 4. Both parent-to-child transmission and affected siblings born to unaffected parents have been reported.


































