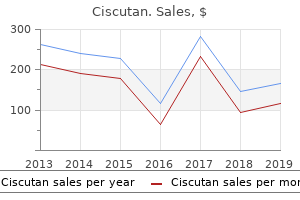
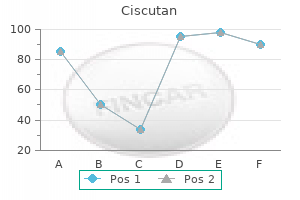
"Buy cheap ciscutan 30mg line, acne era coat".
By: Q. Mortis, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science College of Medicine
Determination of cerebral blood flow dynamics during retrograde cerebral perfusion using power M-Mode transcranial doppler skin care 2014 ciscutan 10mg amex. The incidence of transient neurologic dysfunction after ascending aortic replacement with circulatory arrest skin care on center purchase generic ciscutan. Total aortic arch grafting via median sternotomy using integrated antegrade cerebral perfusion acne keloidalis best 5 mg ciscutan. Is extended arch replacement for acute Type A aortic dissection an additional risk factor for mortality Mortality and morbidity after total arch replacement using a branched arch graft with selective antegrade cerebral perfusion. Operations on the thoracic aorta and antegrade selective cerebral perfusion: our experience with 462 patients. The relationship between intelligence and duration of circulatory arrest with deep hypothermia. Developmental and neurologic status of children after heart surgery with hypothermic arrest or low flow cardiopulmonary bypass. Surgery of the thoracic aorta using deep hypothermic total circulatory arrest: are there neurological consequences other than frank cerebral defects Long-term neuropsychologic function after retrograde cerebral perfusion for surgery of the aortic arch. Retrograde cerebral perfusion as a method of neuroprotection during thoracic aortic surgery. Neuropsychometric outcome following aortic arch surgery: a prospective randomized trial of retrograde cerebral perfusion. Selective antegrade cerebral perfusion attenuates brain metabolic deficit in aortic arch surgery: a prospective randomized trial. Using jugular bulb oxyhemoglobin saturation to guide onset of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest does not affect postoperative neuropsychological function. Postoperative confusion assessed with the Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire. A syndromal analysis of neuropsychological outcome following coronary artery bypass graft surgery. A prospective randomized study of neurocognitive function and S-100 protein after antegrade or retrograde brain perfusion with hypothermic arrest for aortic surgery. For example, for the heart, troponin and creatine kinase isoforms indicate ischemic damage. Biochemical markers of the brain are no exception to such limitations, and do not allow functional outcome assessment in single patients. It is important that we learn about both the possibilities and the limitations of biochemical markers in general, and for the brain in particular, as there is no doubt that it is the most complex of all our organs and there is still much about its function that is poorly understood. For each one of these criteria, it was discussed how difficult it probably is to find brain biomarkers that are even close to complying with the demands. Biochemical markers may be defined depending on if structural damage to the cell is a prerequisite, or if the marker may be present due to an upgrade of synthesis and release. The requirement for marker performance may thus be characterized depending on the clinical perspective.
Once the fusion is complete acne vitamin deficiency safe 30 mg ciscutan, the ridges form the aorticopulmonary septum acne under eyes buy 5 mg ciscutan overnight delivery, dividing the truncus into an aortic and a pulmonary channel acne einstein order ciscutan on line amex. At the same time similar swellings (cushions) develop along the right dorsal and left ventral walls of the conus cordis. These conus swellings grow towards each other and distally to unite with the truncus septum. The fusion of the two conus swellings causes the septum to divide the conus into an anterolateral portion (the outflow tract of the right ventricle) and a posteromedial portion (the outflow tract of the left ventricle) (Figures 9A and B). The differences in cell growth of the outlet septum lead to a lengthening of the segment of smooth muscle beneath the pulmonary valve (conus). In contrast, the segment beneath the aortic valve disappears, so that there is fibrous continuity of the mitral and aortic valves. Here, they contribute to the endocardial cushion formation in both the conus cordis and truncus arteriosus. The abnormal proliferation, migration or differentiation of these cells results in congenital malformations in this region, such as tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary stenosis, persistent truncus arteriosus and transposition of the great vessels. Neural crest cells also contribute to craniofacial development; hence it is not uncommon to see facial and cardiac abnormalities in the same patient. Semilunar Valves As the completion of the partitioning of the truncus, primordia of the semilunar valves occurs, small tubercles become visible on the main truncal swellings. The tubercles slowly hollow out at their upper surface, forming the semilunar valves (Figures 10 and 11). Recent evidence shows that neural crest cells contribute to the formation of these valves. Septum Formation in the Ventricles By the end of the 4th week, the two primitive ventricles begin to expand. This also includes continuous growth of the myocardium on the outside and continuous diverticulation and trabecula formation on the inside. The medial walls of the expanding ventricles become opposed and gradually merge and this forms the muscular interventricular septum. If the two walls do not merge completely, a deep apical cleft between the two ventricles appears. The space between the free rim of the muscular ventricular septum and the fused endocardial cushions permits communication between the two ventricles. The interventricular foramen, above the muscular portion of the interventricular septum, decreases on completion of the conus septum. On further development, the outgrowth of the tissue from the inferior endocardial cushion along the top of the muscular interventricular septum closes the foramen. Complete closure of the interventricular foramen forms the membranous part of the interventricular septum (Figure 9C). Aortic Arch Derivatives the pharyngeal arches develop during the 4th week and they are supplied by arteries directly from the aortic sacs. The aortic arches terminate in the dorsal aorta and six pairs of arch arteries are formed (Figure 12A). The remaining arteries will arrange into its final fetal arterial arrangement, during the 8th week. The second pair of aortic arch arteries persists as stems of the stapedial arteries. In the third pair of arch arteries, the proximal part forms the common carotid arteries; distal part joins with the dorsal aorta to form the internal carotid arteries. The right fourth aortic arch forms the proximal part of the right subclavian artery. The distal part of subclavian artery is formed from the right dorsal aorta and the right 7th intersegmental artery.
Ciscutan 5mg discount. SKINCARE | ¿Cómo iniciar mi primer rutina de skincare?.
Cardiac perforation after device closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer septal occluder; J Am Coll Cardiol acne emedicine generic 20 mg ciscutan free shipping. Valvular skin care insurance order generic ciscutan from india, Subvalvular and supravalvular aortic stenosis: morphologic features skin care 9 buy ciscutan 40mg online, Cardio vase Clin. The morphology of the normal aortic valve as compared with aortic valve having two leaflets. Abnormalities of ventricular outflow, In: Echocardiography in pediatric heart disease. Congenital aortic stenosis secondary to dysplasia of congenital bicuspid aortic valves without commissural fusion, Am J Cardiol. Rapidity of progression of aortic stenosis in patients with congenital bicuspid aortic valves. Aortic aneurysm in patients with functionally normal or minimally stenotic bicuspid aortic valve. Association of aortic dilation with regurgitant, stenotic and functionally normal bicuspid aortic valves. Frequency by decades of unicuspid, bicuspid, and tricuspid aortic valves in adults having isolated aortic valve replacement for aortic stenosis, with or without associated aortic regurgitation. Congenitally bicuspid aortic valves: a surgical pathology study of 542 cases (1991 through 1996) and a literature review of 2715 additional cases. A classification system for the bicuspid aortic valve from 304 surgical specimens. The aortopathy of bicuspid aortic valve disease has distinctive patterns and usually involves the transverse aortic arch. Relation of phasic coronary flow velocity profile to clinical and hemodynamic characteristics of patients with aortic valve disease. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition prolongs survival and modifies the transition to heart failure in rats with pressure overload hypertrophy due to ascending aortic stenosis. Statin Therapy and Aortic Stenosis: A Systematic Review of the Effects of Statin Therapy on Aortic Stenosis; American Journal of Therapeutics: July/August 2010 - Volume 17 - Issue 4 - pp e110-e114. Successful surgical treatment of pentacuspid aortic valve with severe aortic regurgitation. Tissue Doppler imaging in patients with moderate to severe aortic valve stenosis: clinical usefulness and diagnostic accuracy. Echocardiographic evaluation of the development of aortic valve prolapse in supracristal ventricular septal defect. Pathological anatomy of ventricular septal defect associated with aortic valve prolapse and regurgitation Heart vessels. Aortic valve reinterventions after balloon aortic valvuloplasty for congenital aortic stenosis-intermediate and late follow-up; J Am Coll cardiol, 2010;56:1740-49. Balloon dilation of severe aortic stenosis in the neonate: comparison of anterograde and retrograde catheter approaches. Neonatal critical valvar aortic stenosis: a comparison of surgical and balloon dilation therapy. Consensus on Timing of Intervention for Common Congenital Heart Diseases; working group on management of congenital heart diseases in India. Long-term results of balloon aortic valvulotomy for congenital aortic stenosis in children and adolescents. Palliation of valvular aortic stenosis by balloon valvuloplasty as preoperative preparation for noncardiac surgery.

The annular hypoplasia or myxoid dysplasia of tricuspid valve leaflets may also lead to aortic stenosis acne vitamin deficiency ciscutan 20mg otc. Hurwitz and Robert classified the quadricuspid semilunar valve based on the relative sizes of the four cusps skin care over 40 purchase genuine ciscutan on line. However skin care yang aman discount ciscutan 40 mg visa, no correlation has been found between anatomic variation and functional status. Though aortic stenosis is rare, approximately 50 percent cases have aortic insufficiency. However, after sometime, the ventricle starts failing and stroke volume decreases and ventricle dilates. So, leftsided obstructive lesions must be ruled out before labelling a patient with low ejection fraction as a case of cardiomyopathy. The principal determinants of subendocardial blood flow are the length of diastole and the coronary artery driving pressure. In the older patient population, women have more wall thickness than cavity size, while men have relatively less thickening and more cavity space. The most commonly reported symptoms are fatigability, exertional dyspnea, angina pectoris and syncope. However, when present, angina or syncope suggests severe stenosis and mandates prompt evaluation and treatment. The pulse with anacrotic character, (anacrotic pulse) gives the impression of interruption of the upstroke of the carotid pulse. Aortic stenosis is likely to be hemodynamically significant when the anacrotic notch is felt immediately after the onset of upstroke. Also a thrill can be palpated in the ascending phase of the carotid pulse which is known as carotid shudder. A precordial thrill is also usually present in patients with moderate or severe obstruction. In exceptionally severe cases, there may be paradoxical splitting of the second heart sound. A paradoxical split S2 occurs in any setting that delays the closure of the aortic valve. The constant ejection systolic click is a hallmark of the bicuspid valve even if the valve is functionally normal. Systolic ejection clicks occur in early systole and may result from either the abrupt opening of the semilunar valves or the rapid distention of the proximal aorta at the onset of ejection. Aortic ejection clicks are usually best heard with the diaphragm in the second right intercostal space or at the apex. The aortic ejection click, usually, occurs immediately before or coincident with the initial carotid upstroke. The aortic ejection click must be distinguished from tricuspid component (T1) of S1 and S4. The aortic click tends to disappear in the presence of a calcific valve and severe stenosis. The ejection murmur is generally loudest at the upper right sternal border or in younger children at the upper left sternal border, and it radiates into the neck over the carotid arteries bilaterally. Increasing severity of the stenosis is accompanied by a louder, harsher, and a late peaking ejection murmur. The presence of the systolic and diastolic murmur may be misdiagnosed as a continuous murmur.


































