"Cheap asendin 50mg on-line, depression definition and types".
By: S. Kalesch, M.A., Ph.D.
Program Director, State University of New York Upstate Medical University
Dose adjustment for renal dysfunction is necessary only if serum creatinine increases significantly during therapy depression myths order 50 mg asendin mastercard. Amphotericin B has poor cerebrospinal fluid penetration; therefore accompanying meningitis should prompt the addition of 5-flucytosine in doses of approximately 12 depression in men generic asendin 50 mg with mastercard. Peak serum concentrations of this drug should be kept between 40 and 60 g/mL to avoid bone marrow suppression or hepatotoxicity mood disorder awareness ribbon buy discount asendin online. Fluconazole may also be added to amphotericin B for meningeal penetration, if 5-flucytosine is unavailable or cannot be used. Infants being treated with amphotericin B who experience a twofold rise in creatinine, which is evidence of renal tubular compromise or renal tubular acidosis, may benefit from use treatment with one of the liposomal amphotericin preparations. AmBisome has been used in neonates at well-tolerated doses of 5 to 7 mg/kg per dose every 24 hours intravenously, infused over 2 hours (JusterReicher et al, 2003; Weitkamp et al, 1998), although the failure of many liposomal preparations to penetrate renal parenchyma can militate against fungal clearance from this organ. With prompt removal of an offending central venous catheter, and no evidence of dissemination, the duration of therapy for catheter-associated candidemia is typically 10 to 14 days after the blood culture becomes negative (Donowitz and Hendley, 1995). Azoles (such as fluconazole at 6 mg/kg intravenously at varying dosing intervals) are antifungal agents that interfere with ergosterol synthesis by inhibiting C-14 alpha demethylase, a cytochrome P450 enzyme. Azoles such as itraconazole and posaconazole are preferable to fluconazole for aspergillus and zygomycetes, but no studies have been done to recommend neonatal dosing guidelines. Although not a first-line antifungal medication, echinocandins such as caspofungin, which interrupt biosynthesis of -(1,3)-D-glucan, an integral part of the fungal cell wall, have also been used in doses of 1 to 2 mg/kg/day to treat invasive candidal disease in the newborn in several case reports; this drug is particularly helpful for species such as Candida glabrata, Candida krusei or Candida lusitaniae, which may have decreased susceptibility or de novo resistance to amphotericin B (Odio et al, 2004; Saez-Llorens et al, 2009). Fluconazole prophylaxis may have impaired the microbiologic isolation of some fungal species and led to underdiagnosis of infection in the treatment group. This study did not detect a significant effect of fluconazole prophylaxis in reducing invasive candidal disease. Based on these results and cautionary notes, infants weighing less than 1000 g who receive third-generation cephalosporins and central venous catheters may be the best group to be evaluated for a statistically significant benefit of fluconazole prophylaxis in preventing invasive fungal infection, neurologic complications, and death before hospital discharge. Study durations less than 6 years may be insufficient to detect the emergence of fluconazole resistance. Kaufman and Manzoni reported significantly lower incidence of invasive fungal infection, whereas there was no difference in treated versus untreated infants in other studies (Cabrera et al, 2002; Kicklighter et al, 2001; Parikh et al, 2007). The only study to evaluate neurologic outcomes found no difference in neurologic impairment at 16 months (Kaufman et al, 2001). Fluconazole prophylaxis did not create a significant difference in the risk of death before discharge in any of the five studies or in a metaanalysis (Clerihew et al, 2007). No study documented clinically significant adverse effects of fluconazole or the emergence of fluconazole resistance. One study from a single center compared nonrandomized fluconazole prophylaxis in 2002 to 2006 with an untreated, retrospective cohort (2000 to 2001) and reported that invasive candidiasis decreased from 0. Interestingly, fluconazole prophylaxis in this study was extended to several infants with birthweights greater than 1000 g, if risk factors. The finding that prophylactic fluconazole reduces the incidence of invasive fungal infection must be interpreted with caution (Clerihew et al, 2007, 2008): 1. Systemic complications including fungemia, meningitis, or infection of the urinary tract occurred in four of seven confirmed cases and seven of eight probable cases. Diagnosis requires a skin biopsy specimen demonstrating fungal invasion beyond the stratum corneum or a positive potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings; growth of the identical organism from an otherwise sterile site (blood, cerebrospinal fluid, or urine obtained via supra pubic aspiration) is confirmatory. Cutaneous colonization can infect hyperalimentation fluids or parenteral lipid formulations.
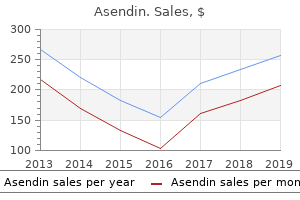
Maternal and fetal conditions that can lead to indicated preterm deliveries include diabetes; hypertension; preeclampsia or eclampsia; maternal cardiovascular and pulmonary disorders; multifetal gestations; uterine structural disorders; polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios; placenta previa definition of depression wikipedia cheap 50mg asendin fast delivery, abruption anxiety disorders association of america generic 50mg asendin with mastercard, and other uterine hemorrhagic events; chorioamnionitis and fetal infection; fetal distress; and congenital anomalies depression test clinical order asendin from india. Allostatic Load Recent studies of the pathophysiology of and biologic responses to stress have uncovered a series of causal pathways for adverse outcomes caused by stresses at multiple levels and from different sources. The biologic responses to stressors have been collectively called allostatic load, a summary measure of major perturbations in the autonomic, endocrine, and immune systems. Allostatic load has been linked to accelerated aging, worsened immunologic tolerance, ineffective defense systems, and increased cardiovascular morbidity. Abnormal allostatic load during the entire life span of a woman can potentially modulate her biologic systems and worsen perinatal outcomes (Groer and Burns, 2009; Herring and Gawlik, 2007; Latendresse, 2009; Lu and Halfon, 2003; McEwen, 2006; Shannon et al, 2007). Studies are under way to understand the complex relationship between the effects of sociodemographic and biologic stressors on organ systems and their influence on perinatal outcomes. The contribution of many factors is noted in Table 14-2 (Behrman and Butler, 2007; Raju, 2006; Raju et al, 2006). Because of the multifactorial nature of preterm labor and birth, it is unlikely that any single intervention could serve to prevent all cases of prematurity. In this section, a number of strategies-both encouraging and disappointing in terms of effectiveness-are described. Etiologic Pathways Preterm labor and delivery arise from abnormal activation of parturition. Progesterone treatment does not appear to pose a developmental risk to the fetus or infant. Cerclage Cervical cerclage is a purse-string suture of the cervix intended to mechanically prevent cervical dilation. A more recent trial indicated a significant beneficial effect (adjusted odds ratio, 0. The proportion of in vitro fertilization cycles in which three or more fresh embryos were transferred declined significantly in the United States between 1996 and 2002 (92% to 54%; p <0. Recent practice guidelines from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine call for wider consideration of single-embryo transfer in many clinical situations (American Society for Reproductive Medicine, 2008). Nevertheless, tocolytic drugs are often used to allow for the administration of steroids and maternal transfer to a facility capable of caring for a preterm neonate. Multifetal Pregnancy Reduction Reduction of multifetal pregnancy, or the selective termination of one or more fetuses in a high-order pregnancy, has been proposed as a means to reduce the risk of prematurity and other pregnancy complications. In addition, antepartum antibiotic treatment decreased the incidence of chorioamnionitis and major morbidity (respiratory distress syndrome, early sepsis, severe intra ventricular hemorrhage, or severe necrotizing enterocolitis) in the infants (Mercer et al, 1997). This bill called for efforts to reduce preterm labor and delivery and the risk of pregnancyrelated deaths and complications, and to reduce infant mortality caused by prematurity. House of Representatives passed the bill unanimously on December 9, 2006, and the president signed it into law on December 22, 2006 (March of Dimes Foundation, 2006). The March of Dimes Foundation initiated the Prematurity Campaign, designed to educate and inform health care professionals, industry, government agencies, and the general public about prematurity-related issues. These and other efforts have begun recently and will take time to yield positive results. As described in other chapters, preterm infants are at greater risk for mortality, and short- and long-term morbidities compared with term infants. A recent study from Norway on the adult-age outcomes of preterm infants reported that even mild prematurity was associated with significantly elevated risk for long-term adverse medical, behavioral, psychological, and vocational outcomes (Moster et al, 2008). The collective economic burden from prematurity was more than $26 billion in 2005 (Behrman and Butler, 2007). The Institute of Medicine of the National Academies of Science issued a major publication providing specific recommendations and guidelines for research, surveillance, and education on this topic (Behrman and Butler, 2007).
Salzman et al (1993) conducted a prospective study in which surveillance cultures of catheter hubs were performed three times per week depression symptoms purchase generic asendin line, and blood cultures and hub cultures were conducted for any suspected episode of sepsis 03 anxiety mp3 purchase asendin cheap online. This mechanism has been confirmed in the neonatal population by Garland et al (2008) depression test long buy asendin with american express. Mahieu et al (2001b) reported that catheter manipulation for blood sampling and fluid or tubing changes raised the risk of colonization. Despite the lack of large randomized controlled trials, the available data suggest that the use of heparin in intravenous fluids is associated with a lower risk of bacterial colonization and thrombosis (Appelgren et al, 1996; Mahieu et al, 2001b). It is hypothesized that heparin prevents bacteria from adhering to the catheter and that the preservatives in heparin preparations have some limited antibacterial properties. Various products have been designed to decrease the risk of catheter-related infection in adult patients. Although data on their use are promising, many of the currently available products are not specifically designed for the neonate, and their safety and efficacy have not been tested in this patient population. Studies are in progress to evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic lock therapy in neonates. In clinical practice, there are numerous approaches to umbilical cord care in the healthy term infant because the available data are insufficient to recommend the use of a specific agent or regimen (Zupan and Garner, 2000). Most authorities agree that the umbilical cord should be separated from the placenta with the use of good aseptic technique. Hexachlorophene and iodine are used sparingly because of concerns about their systemic absorption and toxicity. Unfortunately, this decrease has not clearly resulted in a lower incidence of umbilical cord infections. In a metaanalysis that included "no intervention" as an alternative, Zupan and Garner (2000) were unable to determine which regimen was superior. In general, they found that time to cord separation was prolonged when antiseptics were used, but there were no significant differences in the incidence of infection or death with the use of a particular agent for cord care. The stratum corneum (the outermost layer of skin) has both mechanical and chemical properties that decrease the risk of infection (Darmstadt and Dinulos, 2000). In a prematurely born neonate, the maturation process is accelerated and is usually complete by 2 to 4 weeks after birth (Darmstadt and Dinulos, 2000). Neonatologists had hoped that the application of a topical emollient would protect the developing epidermal layer, reduce the risk of infection, and prevent transepidermal water loss. Forty-six percent (59 of 128) of infants in whom catheter sterilization was attempted had complications, compared with 8% (2 of 25) of those in whom catheters were removed. In particular, infants with gram-negative infections were more likely to have complications if their catheters remained in place. The attempt to retain the catheter was never successful if culture results remained positive for more than 4 days. Additional prospective randomized trials are needed to validate these observational data. As a general rule, antibiotic choice should initially cover a broad spectrum of pathogens and should then be narrowed as soon as possible to cover the specific bacteria identified once sensitivities are known, or it should be discontinued if infection is not proved and is not likely. However, empiric broadspectrum antibiotic use should be limited as much as possible to avoid complications of resistant bacterial and fungal infections. Studies are being conducted in adults to evaluate the efficacy of administering various cytokine preparations known to modulate the inflammatory response. Curtis C, Shetty N: Recent trends and prevention of infection in the neonatal intensive care unit, Curr Opin Infect Dis 21:350-356, 2008. The higher costs are primarily caused by daily hospital charges and pharmaceutical fees (Mahieu et al, 2001a).

Jet ventilators generate a high-velocity gas flow that is injected through a small-diameter tube that opens into the airway connector depression yahoo answers order genuine asendin. Expiration is passive mood disorder spanish buy asendin overnight, and the cycling rate is determined by an electrically operated valve that opens and closes the jet at a predetermined rate and timing anxiety jitters purchase 50mg asendin. The high velocity of the gas injected into the airway produces a Venturi effect that pulls additional gas from the ventilator circuit. This risk is higher when the time constant of the respiratory system is increased by airway obstruction and when large tidal volumes are delivered. Oscillatory ventilators use a piston or a membrane driven by an electromagnetic force and connected to the ventilator circuit. The mean airway pressure is determined by the gas flow through the circuit and a variable resistance, whereas the tidal volume is generated by the size of the excursion of the piston or membrane. It can also be used during bronchoscopy or during airway surgery because in contrast to conventional ventilation, it can produce adequate gas exchange with a partially open airway and large gas leaks (Nutman et al, 1989). Because of the very short inspiratory and expiratory times, it is extremely important to maintain the airway as patent as possible, ensuring a correct position of the endotracheal tube. Any obstruction will produce a decrease in pressure transmission and in tidal volume and can lead to gas trapping. During jet ventilation, it is also critical to ensure proper humidification of the inspired gas to prevent airway damage that can be produced by the high velocity of gas injected into the airway. Higher levels may be necessary in some cases with severe lung disease and poorly compliant lungs. The tidal volume is determined by the delta pressure, and this, in combination with the frequency, determines the Co2 elimination. The pressure transmission to the distal airways is greatly influenced by the resistance of the tube and the airway, so only a small fraction of the delta pressure generated by the ventilator is transmitted to the terminal airspaces. This combination of factors explains why they frequently become ventilator dependent for long periods of time. For many years, infants who were ventilated received most of their minute ventilation from the ventilator and were not allowed to have effective spontaneous ventilation. Because of the high rate of complications associated with prolonged mechanical ventilation, weaning should start as soon as respiratory function is stabilized. The order in which the different ventilator parameters are decreased is determined by the relative risk of complications associated with each of them. The ideal ranges of oxygenation have not been defined, but most clinicians accept saturations between 88% and 95% in preterm infants and up to 98% in term infants. In infants with evidence of pulmonary hypertension, higher levels are targeted to prevent pulmonary vasoconstriction. The ventilator rate is adjusted depending on the type of ventilation strategy being used. Therefore, this rate is only relevant when the infant becomes apneic or hypoventilates. When the infant is controlled, the rate in the ventilator is not determined by the infant, and the adjustment in mechanical rate is based on the arterial Pco2 level. During weaning, it is advisable to do gradual changes and adjust one parameter at a time to evaluate the response of the infant to each change.
An example of a soft marker for trisomy 18 is the presence of choroid plexus cysts anxiety xanax and dementia order asendin canada. Therefore the presence of choroid plexus cysts anxiety jesus buy asendin with amex, with other soft markers such as echogenic bowel anxiety kids symptoms generic 50mg asendin visa, single umbilical artery, or both, in association with an omphalocele or a neural tube defect, would strongly increase the suspicion of fetal trisomy 18. Three-dimensional sonography improves detection of cleft palate, and magnetic resonance imaging improves assessment of fetal brain anomalies. To date, two main clinical applications have transitioned from bench to bedside: fetal rhesus D genotyping (Bianchi et al, 2005) and fetal gender determination (Rijnders et al, 2001). Both have been routinely available in the United Kingdom and Europe for a number of years and are just beginning to be available in the United States (Hill et al, 2010). The rate of clubfoot in the early amniocentesis group was tenfold the risk in the general population. The cause of clubfoot is thought to be a disruption of normal foot development secondary to transient oligohydramnios (Farrell et al, 1999). The fact that the procedure is performed early is advantageous, because most women at this point do not have external manifestations of pregnancy and have not yet perceived fetal movement. The chorionic villi are composed of syncytiotrophoblast and mesenchymal core cells that are actively growing and dividing. In contrast to the dying epithelial cells shed into the amniotic fluid, chorionic villus cells do not require prolonged culture to provide enough mitoses for a cytogenetic diagnosis. Initially, direct preparations derived from syncytiotrophoblast were used for analysis, but the number of apparently mosaic abnormal results proved unacceptable. Cultured preparations derived from the cell of the mesenchymal core are more closely related in embryonic origin to the actual fetus (Bianchi et al, 1993). It is currently recommended that both direct and cultured preparations be used for cytogenetic analysis. With the transcervical technique, the inherent risks of fetal and maternal infection appear to be greater, because it is impossible to sterilize the cervix. Under ultrasonographic guidance, a flexible catheter is passed through the endocervix and placed into the chorion frondosum. A small segment of placenta is then aspirated into sterile tissue culture medium, and the catheter is withdrawn (Jackson, 1985). In contrast, the transabdominal technique uses a needle to obtain villus material; sterilization of the skin surface is straightforward (Brambati et al, 1988). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health held a consensus conference to summarize worldwide experience. The 1% incidence of mosaicism in villus samples may necessitate a further invasive technique, such as amniocentesis or cordocentesis, to confirm or refute diagnoses. Uniparental disomy refers to the inheritance of both copies of a chromosome pair from a single parent. One third of the time, the fetus will be left with two chromosomes that originated in a single parent. Uniparental disomy is an important mechanism in conditions such as Prader-Willi syndrome. This number is reasonably similar to that in population-based registries that monitor infants with all limb deficiencies, which give a rate of 5 to 6 per 10,000 live births (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1995).
Purchase discount asendin on line. tattoos cure depression.


































